Fighting Fungi by Capturing Sugars
Scientists from the Yale Chemistry Department have developed a new small molecule that bolsters the body’s own immune system against fungal infections.

Scientists from the Yale Chemistry Department have developed a new small molecule that bolsters the body’s own immune system against fungal infections.

In the aftermath of Hurricane Maria, researchers are striving to save the unique monkey population near Puerto Rico.

Survival of the fittest isn’t the end of the story. New research by Yale scientists shows that weak species are able to grow with stronger species, and the presence of weak species may help ecosystems respond to climate change.

Despite advances in modern medicine, many respiratory and mosquito-borne viruses still have few treatment options. SPCA1, a calcium transporter required in the viral life cycle, may be a potential target to eliminate viruses such as RSV, Zika, and West Nile.
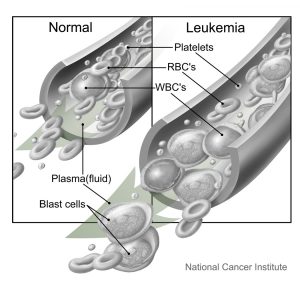
Tet2, a gene believed to be a tumor suppressor since 2009, may also have tumor-promoting effects on other types of cancer, raising some interesting questions about what it means to be a tumor suppressor and how Tet2 could affect different cancer treatments.
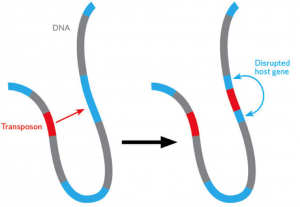
New technology that enables certain segments of DNA to “jump” around the genome via a cut and paste method can serve as a more cost-effective, time-efficient alternative to using STEM cells

Professor Jim Mayer was recently named one of the winners of the 2018 ACS Award in Inorganic Chemistry and has published multiple papers in 2017. His lab focuses on synthesis of new molecules, analysis of their structure and properties, and study of their chemical reactivity.
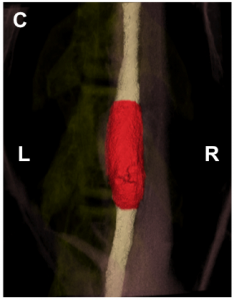
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of disease and death in the U.S, yet patients with faulty arteries are forced to deal with synthetic arterial grafts that degrade slowly, prompting further invasive treatment that costs patients, families, and medical personnel time and money. Ramak Khosravi, MD/PhD candidate at Yale, has come up with a method that she hopes will produce a graft that can seamlessly integrate into human bodies.
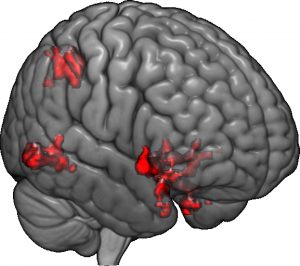
A study published in PNAS in August 2017 showed how the mistiming of someone’s thoughts may be linked to a person’s tendency to hold delusional thoughts.

Yale researchers have unveiled a new cryo-electron microscope, able to probe within the structure of proteins.

The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project aims to characterize the gene expression profiles of different human tissues. The resulting gene expression map could help clarify how genetic variations work at a molecular level to influence gene expression.

Hermit crabs are typically associated with occupying molluscan shells. However, a newly discovered species of hermit crab in the Oshima Strait was found inhabiting walking corals; these corals were previously thought to house only sipunculan worms.